Article
Sovereignty-Association
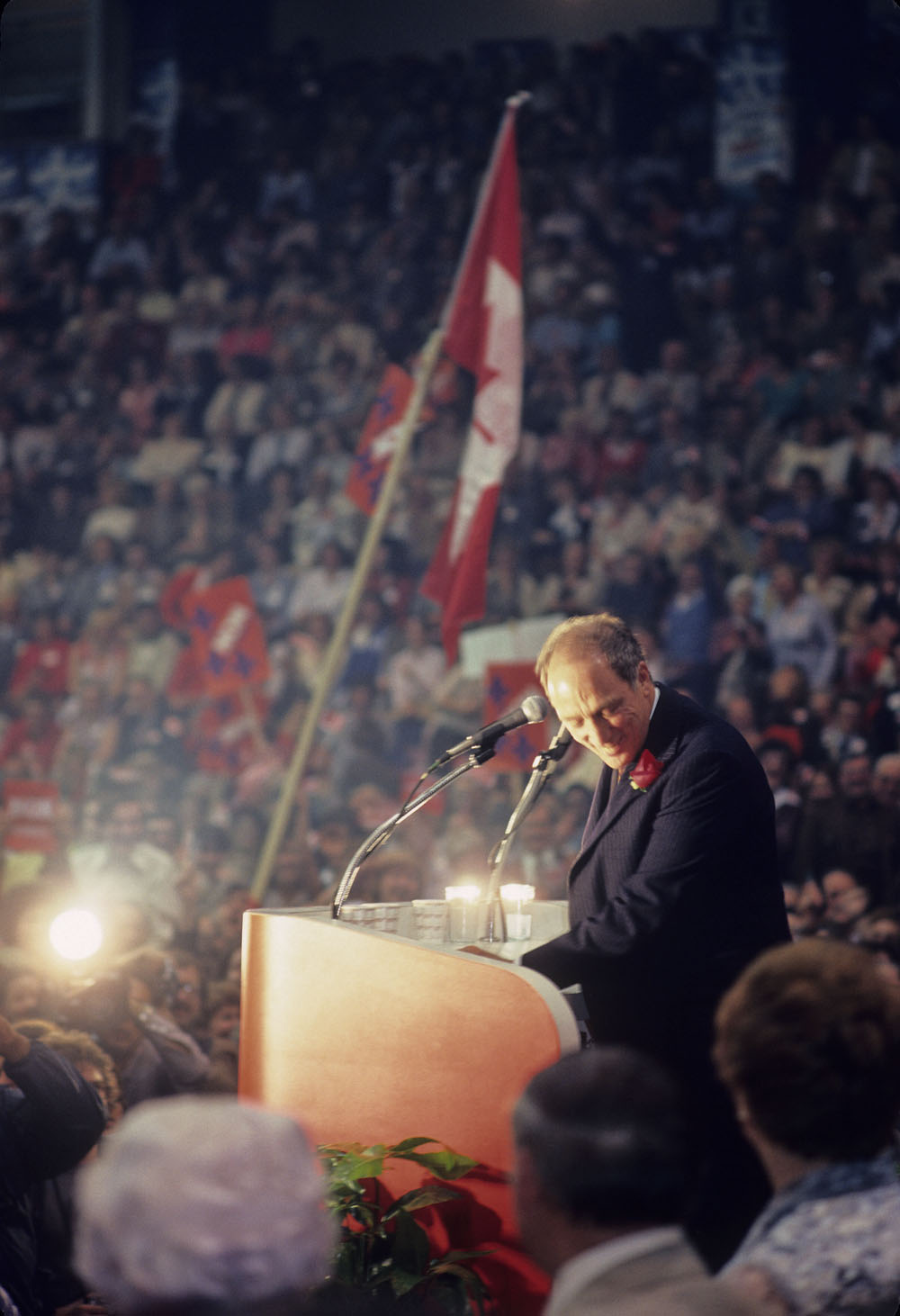
First used as a slogan by the Mouvement Souveraineté-Association (MSA), forerunners of the Parti Québécois, this term became the PQ’s cornerstone and main objective.

Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create AccountArticle
First used as a slogan by the Mouvement Souveraineté-Association (MSA), forerunners of the Parti Québécois, this term became the PQ’s cornerstone and main objective.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/cf2ba193-435f-4280-85a0-88632e234b1d.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/cf2ba193-435f-4280-85a0-88632e234b1d.jpg

Article
The SS Queen Victoria played host to crucial discussions about Confederation in Charlottetown harbour in 1864. Two years later, the ship was lost in a hurricane off Cape Hatteras. The wreckage has never been found.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/7c6fd58d-8f6a-4557-baf5-d9d38ea623ff.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/7c6fd58d-8f6a-4557-baf5-d9d38ea623ff.jpg

Article
Statute of Westminster, 1931: DocumentSelected text of the Statute of Westminster:An Act to give effect to certain resolutions passed by Imperial Conferences held in the years 1926 and 1930 Whereas the delegates to His Majesty's Governments in the United Kingdom, the Dominion of Canada, the Commonwealth of Australia, the Dominion of New Zealand, the Union of South Africa, the Irish Free State and Newfoundland, at Imperial Conferences holden at Westminster in the years of our...
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. In the fall of 1929, Canada’s Minister of Justice, Ernest Lapointe, travelled to England. He took with him Dr. Oscar Skelton — the “elder statesman” of the Canadian civil service, as William Lyon Mackenzie King once described him. When Lapointe and Skelton were done their negotiations, they had confirmed that Canada would have its independence from the British Empire.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/43cb3921-bb9b-4a07-818d-0f1dfeb80b26.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/43cb3921-bb9b-4a07-818d-0f1dfeb80b26.jpg

Article
Women’s suffrage (or franchise) is the right of women to vote in political elections; campaigns for this right generally included demand for the right to run for public office. The women’s suffrage movement was a decades-long struggle to address fundamental issues of equity and justice. Women in Canada, particularly Asian and Indigenous women, met strong resistance as they struggled for basic human rights, including suffrage. Representative of more than justice in politics, suffrage represented hopes for improvements in education, healthcare and employment as well as an end to violence against women. For non-white women, gaining the vote also meant fighting against racial injustices. (See also Women’s Suffrage Timeline.)
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/88bab6f6-366c-45d5-be02-092e23d46e97.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/88bab6f6-366c-45d5-be02-092e23d46e97.jpg

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. The Baldwin–LaFontaine government of 1848 has been called the “great ministry.” In addition to establishing responsible government, it had an incomparable record of legislation. It established a public school system and finalized the founding of the University of Toronto. It set up municipal governments and pacified French-Canadian nationalism after a period of unrest. Responsible government did not transform Canada overnight into a fully developed democracy. But it was an important milestone along the road to political autonomy. Most importantly, it provided an opportunity for French Canadians to find a means for their survival through the British Constitution. The partnership and friendship between Baldwin and LaFontaine were brilliant examples of collaboration that have been all too rare in Canadian history.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ba6bdff6-574a-4697-ac95-afdcc5ddfcc9.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/ba6bdff6-574a-4697-ac95-afdcc5ddfcc9.jpg

Article
One of the great, unheralded events in Canadian history took place in September 1841 at an annual feast and ceremony of Illumination at Sharon Temple, meeting place for the Children of Peace.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/Responsible government.png" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/Responsible government.png

Macleans
Like many other Torontonians last Friday, Mayor Barbara Hall just wanted to go to work. But when she showed up at the front entrance to City Hall around 8 a.m.This article was originally published in Maclean's Magazine on November 4, 1996
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Treaty-Making Power describes any and all types of international agreements governed by international law which are concluded between and among states and international organizations. Terms such as "convention," "protocol" and "declaration" are sometimes used to describe such agreements.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
On 8 November 1861, seven months after the onset of the American Civil War, American Captain Charles Wilkes stopped RMS Trent, an unarmed British ship, in international waters between Cuba and the Bahamas. He took two Confederate envoys prisoner. The incident led to a diplomatic crisis between Britain and the United States that nearly led to a war that would have involved Canada. The Trent Affair was peacefully resolved when the two envoys were released on 1 January 1862 and allowed passage to Britain.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/TrentAffair/Trent_affair-boarding.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/TrentAffair/Trent_affair-boarding.jpg

Article
The Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) started working in 2008. It was a result of the Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement (IRSSA). The IRSSA recognized the suffering and trauma experienced by Indigenous students at residential schools. It also provided financial compensation (money) to the students. The TRC performed many tasks. It created a national research centre. It collected documents from churches and government. It held events where students told their stories. Also, it did research about residential schools and issued a final report. (See also Reconciliation in Canada.)
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/2bd71aaf-ebc5-44e0-9f91-e4d07b16e81d.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/2bd71aaf-ebc5-44e0-9f91-e4d07b16e81d.jpg
Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. Before Confederation, the right to vote in elections was restricted to a small, wealthy, property-owning elite. Because votes were declared publicly, elections were rowdy, highly competitive and even violent. Voting by secret ballot was first introduced in New Brunswick in 1855 and federally in 1874.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1e88decf-02d6-4b89-b522-383f360ecac4.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1e88decf-02d6-4b89-b522-383f360ecac4.jpg

Macleans
The vote was close, nail-bitingly close. Last week, Polish voters narrowly elected a smooth-faced, smooth-talking former Communist to the presidency of Poland, ousting Nobel Peace Prize winner Lech Walesa and ending an era in Polish politics.This article was originally published in Maclean's Magazine on December 4, 1995
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
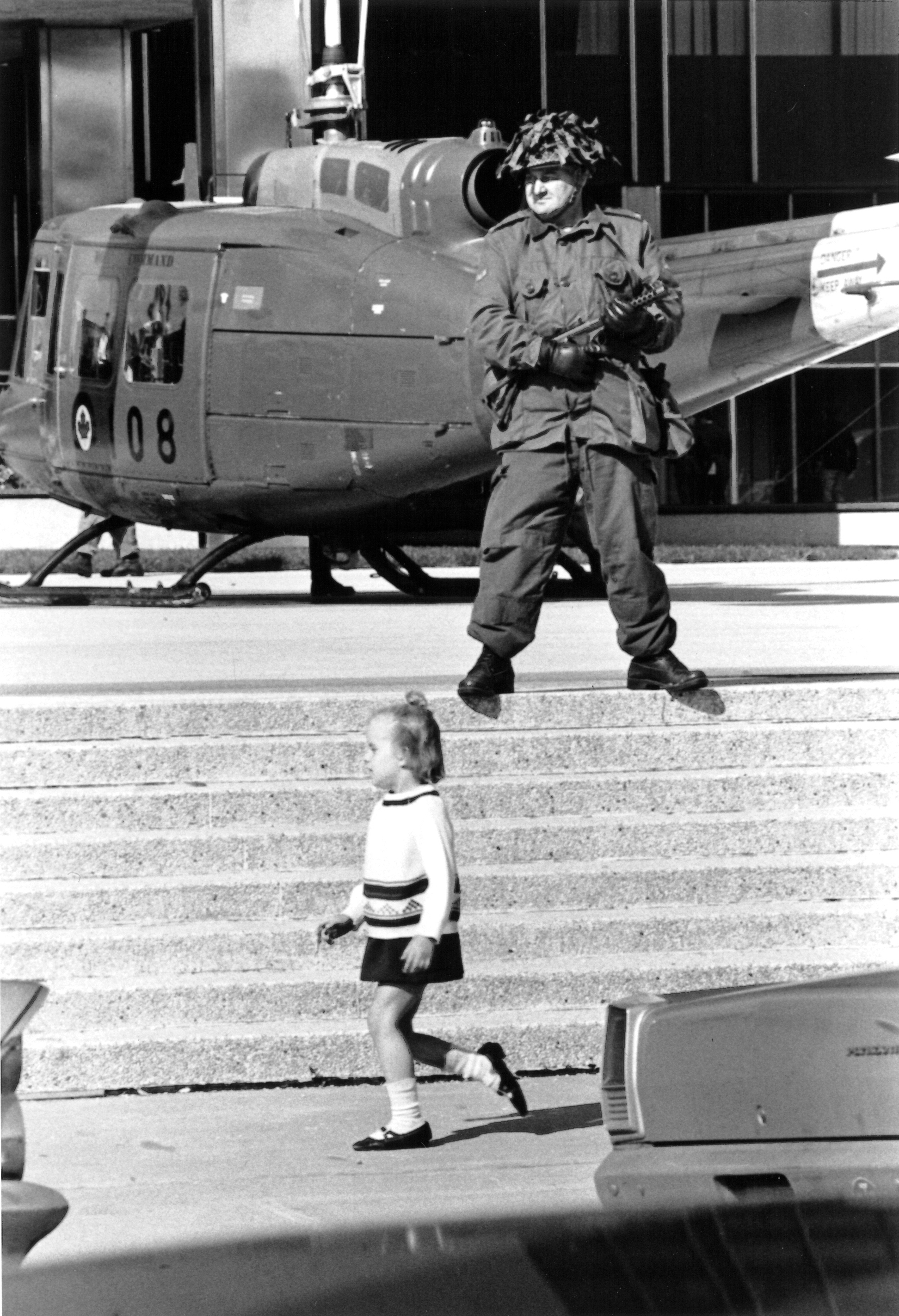
The War Measures Act was a federal law adopted by Parliament on 22 August 1914, after the beginning of the First World War. It gave broad powers to the Canadian government to maintain security and order during “war, invasion or insurrection.” It was used, controversially, to suspend the civil liberties of people in Canada who were considered “enemy aliens” during both world wars. This led to mass arrests and detentions without charges or trials. The War Measures Act was also invoked in Quebec during the 1970 October Crisis. The Act was repealed and replaced by the more limited Emergencies Act in 1988.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/c8a1d56b-60f5-40b0-86e2-3ce31bc3e7b0.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/c8a1d56b-60f5-40b0-86e2-3ce31bc3e7b0.jpg

Article
The Wartime Elections Act of 1917 gave the vote to female relatives of Canadian soldiers serving overseas in the First World War. It also took the vote away from many Canadians who had immigrated from “enemy” countries. The Act was passed by Prime Minister Robert Borden’s Conservative government in an attempt to gain votes in the 1917 election. It ended up costing the Conservatives support among certain groups for years to come. The Act has a contentious legacy. It granted many women the right to vote, but it also legitimized in law many anti-immigrant sentiments.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/6e19f5db-f5f6-4776-baf8-40a98b38b97d.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/6e19f5db-f5f6-4776-baf8-40a98b38b97d.jpg
