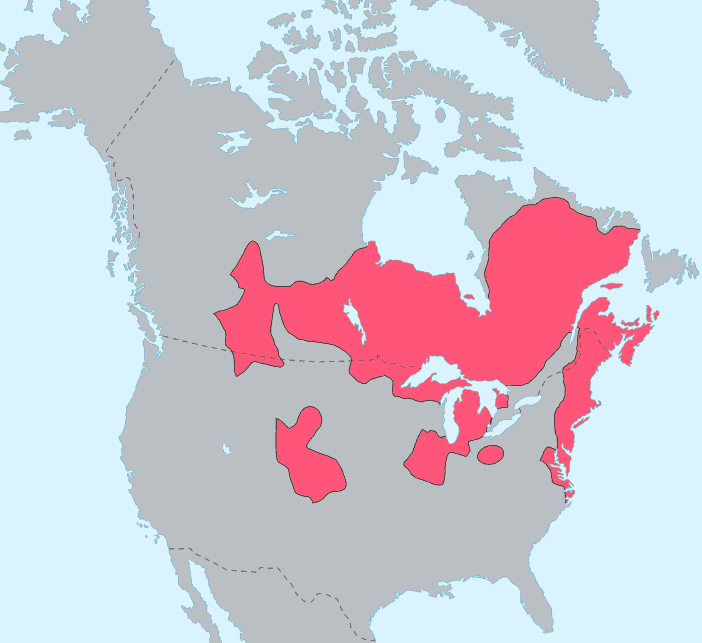
Algonquian describes an ethno-cultural and linguistic group of Indigenous peoples that historically lived in the Eastern Woodlands. This is a region that stretches from the northeastern coast of present-day United States and the Maritimes to west of the Great Lakes. Algonquian-speaking peoples are also found in western Canada. Some Indigenous nations described as Algonquian include the Anishinaabeg, Abenaki, Odawa, Innu, Wolastoqiyik (Maliseet) and Mi’kmaq.
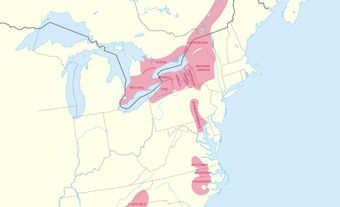
Algonquian is not to be confused with Algonquin. The term Algonquin refers to an Indigenous population with its own language and culture. Algonquian refers to a much larger grouping of Indigenous nations, including the Algonquin people.
Algonquian nations have similar cultural practices, spiritual beliefs and political structures. For example, many Algonquian nations are patrilineal and organized by a band system. Algonquian peoples also generally practiced Midewiwin (Grand Medicine Society), which is still practiced today. Neighbouring Algonquian nations historically traded and visited with one another. However, these nations are not monolithic. Each Algonquian nation has its own unique characteristics, affected by its own history and oral tradition, geography, and culture.
Within the Eastern Woodlands, there are two branches of the Algonquian linguistic family, Central Algonquian (Ojibwe, Odawa, Nipissing and Algonquin) and Eastern Algonquian (Abenaki, Mi’kmaq and Maliseet). (See also Anishinaabemowin: Ojibwe Language.) Languages within each branch show a high degree of mutual intelligibility, with the Central Algonquian forming dialect chains. Algonquian languages are also found in the Canadian Prairies and midwestern United States, including the languages of the Blackfoot Confederacy. (See also Siksikáí’powahsin: Blackfoot Language.) According to the 2016 census, the Algonquian language group is the largest in Canada, with approximately 175,825 speakers. The majority of these speakers reside in Manitoba (21.7%); the rest live in Quebec (21.2%), Ontario (17.2%), Alberta (16.7%) and Saskatchewan (16.0%).

 Share on Facebook
Share on Facebook Share on X
Share on X Share by Email
Share by Email Share on Google Classroom
Share on Google Classroom