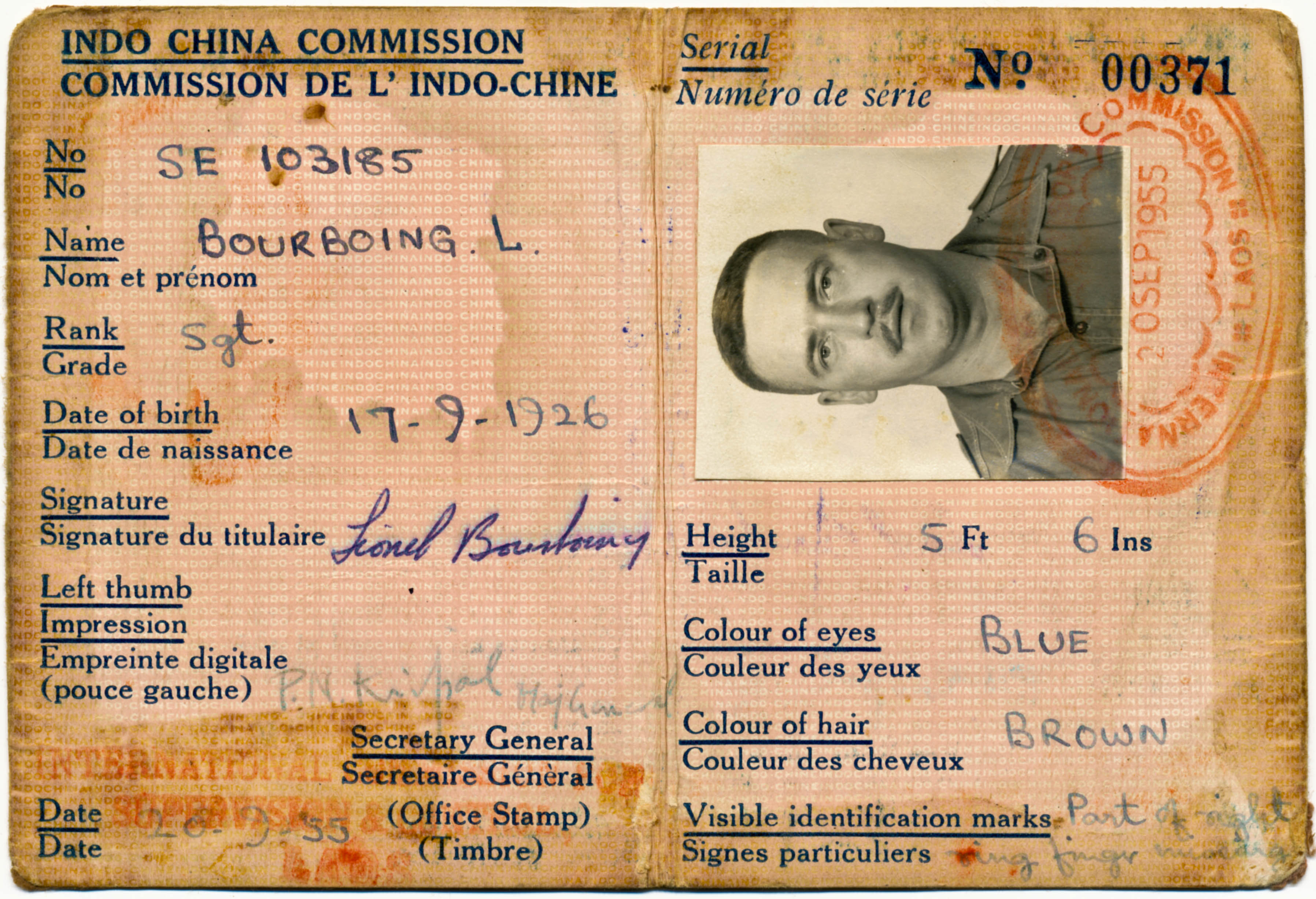
Memory Project Archive
Lionel Bourboing (Primary Source)
Please be advised that Memory Project primary sources may deal with personal testimony that reflect the speaker’s recollections and interpretations of events. Individual testimony does not necessarily reflect the views of the Memory Project and Historica Canada.